Using Reusable Functions
Reusable functions can be called from multiple locations in your Wized project. This page explains how to invoke functions in different contexts.
Function Mode Selection
Wherever you can run custom JavaScript code (in events and workflows), you'll see a Function Mode option that lets you choose between:
- Inline function - Write code directly in the action (default for most cases)
- Select function - Choose a predefined function and pass values to its props
Using Functions in Global Events
Global events can trigger reusable functions in response to page-level events.
Steps:
- Navigate to Global Events in the left sidebar
- Create or edit a global event
- Add a Run Function action
- Set Function Mode to "Select function"
- Choose your function from the Function dropdown
- Configure the function props with the values you want to pass
Example:
Create a global event that validates and processes a form submission:
Trigger: After request
r.submitContactFormsucceedsAction: Run Function
Function:
processContactSubmissionProps:
javascript// formData prop return r.submitContactForm.data; // successMessage prop return 'Thank you for contacting us!';
Using Functions in Element Events
Element events can call functions when users interact with specific elements.
Steps:
- Select an element in your project
- Open the Element Events panel
- Add an event (e.g., click, submit, etc.)
- Add a Run Function action
- Set Function Mode to "Select function"
- Select your function and configure props
Example:
Add a click event to a button that formats and displays user input:
- Element: Button with attribute
wized="formatButton" - Event: click
- Action: Run Function
- Function:
formatAndDisplay - Props:
inputValue:
return i.userInput.value;formatType:
return 'currency';Using Functions in Workflow Nodes
Workflows can call functions as part of a sequence of actions.
Steps:
- Open your workflow
- Create or select an Action Node
- Set the node type to Run Function
- Set Function Mode to "Select function"
- Choose your function from the dropdown
- Configure the function props
Example:
Lets define a function with name validate-user-create-data with props: email and password and code:
if (p.password.length < 8) {
return {
valid: false,
message: 'Password should have more than 8 characters!',
};
}
return {
valid: true,
};In a user registration workflow:
Node: Action
Type: Run Function
Function:
validate-user-create-dataProps:
javascript// email prop return p.email; // Using workflow prop // password prop return p.password; // Using workflow prop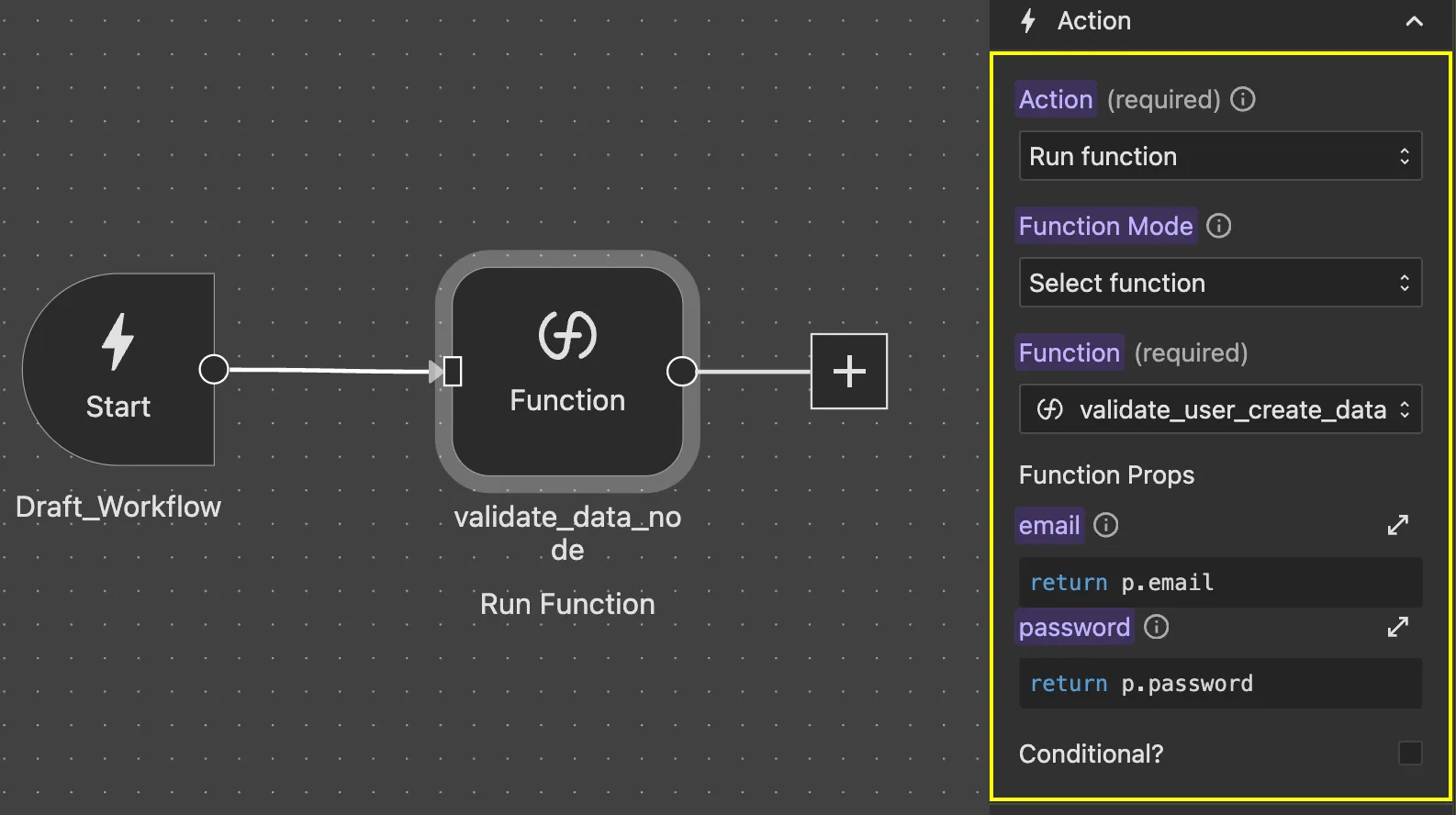
You can then access function result in the next if else node
return w.Register_user.nodes.validate_data_node.result.valid;or the message
return w.Register_user.nodes.validate_data_node.result.message;When to Use Inline vs Reusable Functions
Use Inline Functions When:
- The logic is simple and specific to one place
- The code is unlikely to be reused elsewhere
- You want to quickly prototype without creating a separate function
- The logic is tightly coupled to the specific event or workflow
Use Reusable Functions When:
- The same logic needs to be used in multiple places
- The function performs a distinct, well-defined task
- You want to maintain consistency across your project
- The logic is complex enough to benefit from centralized maintenance
- You want to improve code organization and readability
Common Use Cases
Form Validation
Create reusable validation functions for email, phone numbers, passwords, etc., and call them from multiple form submissions.
Data Formatting
Build functions to format dates, currencies, addresses, or other data types consistently across your project.
API Response Processing
Centralize logic for processing API responses, extracting data, and handling errors.
User Notifications
Create functions that display messages or notifications in a consistent way throughout your application.
State Management
Build functions that update multiple related variables or perform complex state changes.
Best Practices
- Name functions clearly - Use descriptive names that indicate what the function does
- Keep functions focused - Each function should do one thing well
- Return meaningful values - Always return data that can be useful to the caller
- Handle errors gracefully - Use try/catch blocks and return error indicators
- Document complex logic - Add comments to help others (and future you) understand the code
- Test thoroughly - Verify functions work correctly with different prop values
- Organize with folders - Group related functions together for easy management